Fargo is an expanding city in North Dakota, USA that is home to increasing entrepreneurship and innovative pursuits. However, it is also a city that experiences drastic climate changes throughout the year; both temperature and sun path see large variations depending on the season. Many commercial buildings in the area spend large amounts on energy to keep the inside of the building at a comfortable ambient temperature and appropriately lit. This project seeks to explore the creation of a net-zero start-up building, with focus on reducing energy consumption and creating a comfortable atmosphere for its occupants.
The initial lot was chosen to be a vacant parking lot surrounded by businesses, convenient venues, and recreational spaces. Surrounding massing was created in Rhino, and Diva in Grasshopper was used to analyze the sun path and resulting shadows on the lot over the course of a year. Below is a compiled sun path and shading at 9 am, 1 pm, and 5 pm respectively on the 1st of January, April, July, and October.


In designing the building form, focus was on complementing surrounding geometries and creating an open concept. The building form reflect the basic trapezoidal shape of the lot, and the two stories reflect the height of the neighboring buildings. The client request was for the space to be 2500 square meters. The space will host a variety of dynamic interactions and the second floor workspace can be occupied at all hours. An open concept can adapt to user needs, while allowing for reception and cafe spaces on the first floor and work space and conference rooms on the second floor. There are also disability accommodations.






Static shades were placed in the windows at 54 degrees to reduce glare while allowing for daylight to reach far into the space. Lighting was supplemented with artificial lighting over the main workspace, and analysis was conducted to make sure it is within comfortable range. Roof placement of solar panels allows for the building to reduce energy costs with an expected payback time of only 3.25 years. Solar panels were angled on the roof at 43 degrees. This tilt is optimal for solar panels in North Dakota that experience no shadow coverage from surrounding buildings.

1st floor w/o shading
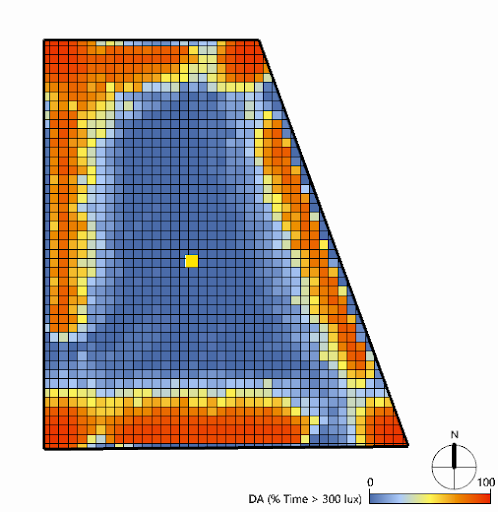
1st floor w/ shading

2nd floor w/o shading

2nd floor w/ shading

2nd floor glare w/o shading

2nd floor glare w/ shading

Plan view of solar panel placement
Target EUI (energy use intensity) was 126 kWh/m squared. Our building has an EUI of 123.46 kWh/m squared. In order to create a tight building envelope, windows are double paned, there is dense insulation (R30 in roof and R19.5 in walls), and doors are weatherstripped. Use of ground source heat pumps (geothermal heat pumps) will lower EUI by an additional 18 kWh/m squared.
4.401 Environmental Tech in Buildings
Professor Christoph Reinhart
Collaborators: Seif Eses, Stephanie Li
Fall 2019